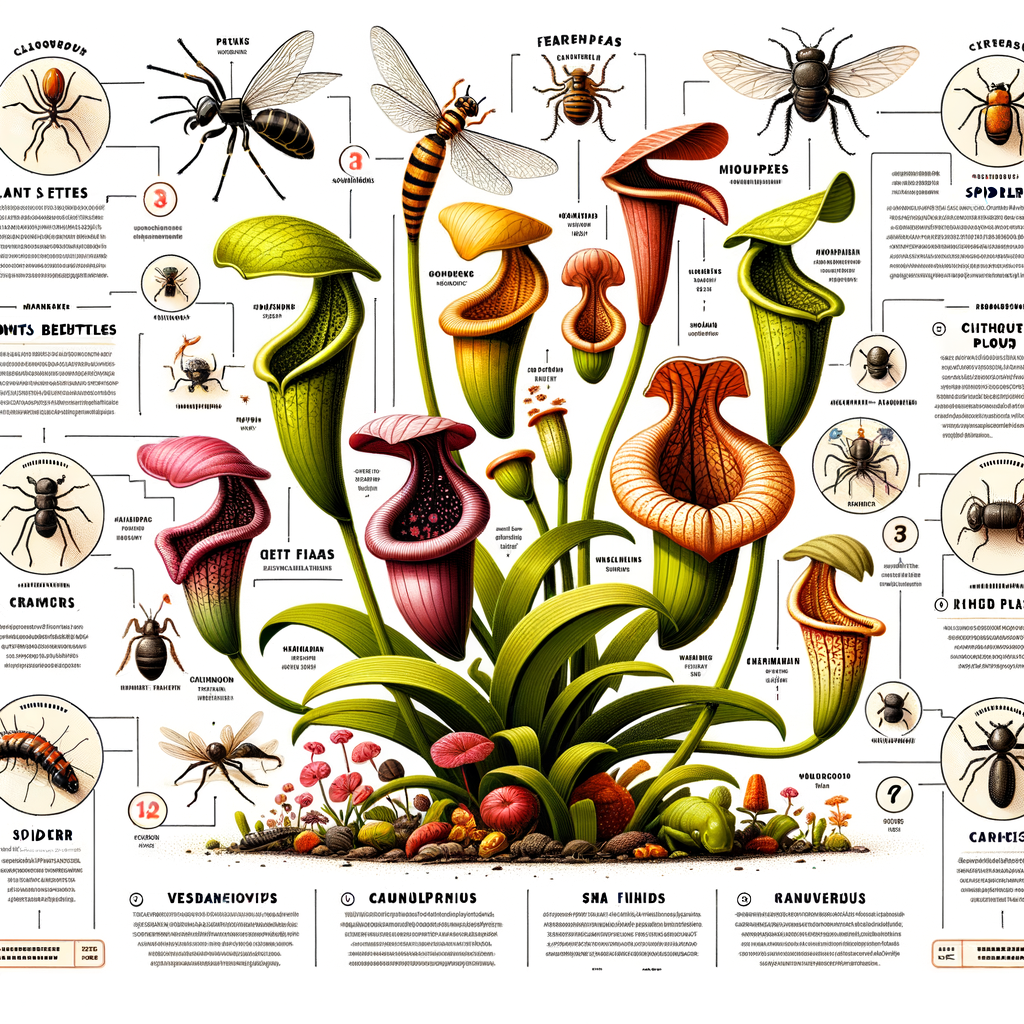
Introduction to Pitcher Plants
Welcome to the fascinating world of pitcher plants! These unique plants are unlike any other you might find in your backyard. They are carnivorous, meaning they eat meat. But don’t worry, they don’t eat humans or pets. Instead, they feast on insects and small animals. Let’s dive in and learn more about these amazing plants.
- Understanding Pitcher Plants
- Diet of Carnivorous Plants
Pitcher plants are named for their unique shape, which resembles a pitcher or jug. They are part of a group of plants known as carnivorous plants. These plants have evolved to thrive in environments where the soil is poor in nutrients. To make up for this, they have developed the ability to catch and digest insects and other small creatures.
The pitcher plant’s leaves have adapted to form a deep cavity filled with digestive fluid. The plant lures its prey into this “pitcher” with sweet nectar. Once the insect is inside, it can’t climb back out because of the slippery walls and it eventually drowns in the fluid at the bottom. The plant then absorbs the nutrients from the decomposed insect.
As we’ve learned, pitcher plants are carnivorous, which means they eat meat. But what exactly does their diet consist of? The majority of their food comes from insects like flies, beetles, and spiders. Some larger species of pitcher plants have been known to catch and digest small frogs and mice!
It’s important to note that while these plants are carnivorous, they can also photosynthesize like other plants. This means they can make their own food from sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. The insects and small animals they catch provide them with extra nutrients that they can’t get from the soil or from photosynthesis.
Pitcher Plants Diet
One of the most fascinating aspects of pitcher plants is their unique diet. Unlike most plants, pitcher plants are carnivorous, meaning they eat meat. But what exactly does this diet consist of? Let’s delve deeper into the world of pitcher plants and their intriguing dietary habits.
What Pitcher Plants Eat
Pitcher plants have a varied diet, but their primary source of food comes from the insect world. They also have been known to consume other small creatures, including fish. Here’s a closer look at what these carnivorous plants eat:
- Insects Eaten by Pitcher Plants
- Pitcher Plants and Fish Food
Pitcher plants are known for their ability to trap and digest a wide variety of insects. These include flies, beetles, ants, and even spiders. The plant’s unique pitcher-shaped leaves, filled with a sweet-smelling nectar, lure insects into the trap. Once inside, the insects are unable to escape due to the slippery walls and downward-facing hairs of the pitcher. They eventually drown in the liquid at the bottom of the pitcher, which contains enzymes that break down the insect’s body into nutrients the plant can absorb.
While insects make up the bulk of a pitcher plant’s diet, they have also been known to consume small fish. This is more common in larger species of pitcher plants that grow near bodies of water. The fish are attracted to the plant’s nectar, just like insects, and once they fall into the pitcher, they are unable to escape. The plant then uses its enzymes to digest the fish, absorbing the nutrients it needs to survive.
In conclusion, the pitcher plant’s diet is a fascinating example of nature’s ingenuity. These plants have adapted to their nutrient-poor environments by evolving a unique way of obtaining the nutrients they need – by becoming carnivorous. Whether it’s an unsuspecting insect or a small fish, the pitcher plant’s diet is a testament to the adaptability and diversity of life on Earth.
Feeding Habits of Pitcher Plants
Pitcher plants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to thrive in environments where most plants struggle. Unlike most plants, they don’t rely solely on sunlight and soil nutrients for survival. Instead, they have developed a unique feeding habit that involves trapping and digesting insects and other small creatures. This carnivorous behavior allows them to supplement their diet and survive in nutrient-poor soils.
Types of Food for Pitcher Plants
Pitcher plants are not picky eaters. They can consume a wide range of prey, from insects like ants, beetles, and spiders to larger creatures like frogs and even small birds. The type of prey they capture often depends on their size and location.
- Prey Capture Mechanisms
- Process of Digestion
Pitcher plants use a variety of mechanisms to capture their prey. The most common is their pitcher-shaped leaves filled with a sweet-smelling nectar. This nectar attracts insects and other small creatures. Once the prey lands on the slippery rim of the pitcher, it slides down into the trap where it becomes trapped in a pool of digestive enzymes.
Once the prey is trapped, the digestion process begins. The pitcher plant releases enzymes that slowly break down the prey. This process can take anywhere from a few days to a couple of weeks, depending on the size of the prey. The nutrients from the digested prey are then absorbed by the plant, providing it with essential nutrients that it can’t get from the soil.
In conclusion, the feeding habits of pitcher plants are a fascinating example of nature’s adaptability. These plants have evolved to become efficient hunters, using their unique structures and mechanisms to capture and digest a wide range of prey. This allows them to thrive in environments where other plants would struggle.
Pitcher Plant Nutrition
While pitcher plants are known for their carnivorous feeding habits, they still require sunlight for photosynthesis like other plants. The nutrients they gain from their prey supplement their diet, providing them with essential elements like nitrogen and phosphorus that are often lacking in the poor soils where they grow.
Case Studies: Pitcher Plants in Action
There are many fascinating case studies of pitcher plants in action. For example, the Bornean pitcher plant (Nepenthes rajah) is known to capture not only insects but also small mammals like rats. Another interesting case is the Parrot Pitcher Plant (Sarracenia psittacina) which uses its brightly colored leaves and sweet-smelling nectar to attract and trap frogs.
Key Takeaways: Understanding Pitcher Plants’ Diets
To understand the diet of pitcher plants, it’s important to remember that they are not solely carnivorous. They still require sunlight for photosynthesis and gain additional nutrients from the prey they capture and digest. Their unique feeding habits are a testament to nature’s adaptability and creativity.
Conclusion: The Fascinating World of Carnivorous Plants
The world of carnivorous plants is truly fascinating. From their unique structures to their ingenious prey capture mechanisms, these plants are a testament to the wonders of nature. As we continue to study them, we can learn more about their diets and how they have adapted to survive in some of the world’s harshest environments.
Pitcher Plant Nutrition
Understanding the nutrition of pitcher plants is crucial to appreciate their unique survival strategy. These carnivorous plants have developed a remarkable way to supplement their diet, which sets them apart from most other plant species. Let’s delve into the nutritional benefits of their carnivorous diet and the role of insects and fish in their nutrition.
- Nutritional benefits of the carnivorous diet
- Role of insects and fish in the plant’s nutrition
The carnivorous diet of pitcher plants offers several nutritional benefits. Unlike most plants, which rely solely on photosynthesis, pitcher plants supplement their diet with nutrients from insects and sometimes small fish. This adaptation allows them to thrive in nutrient-poor soils where other plants struggle to survive.
When insects or small fish fall into the pitcher plant’s trap, they are broken down by enzymes and bacteria. This process releases essential nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which the plant absorbs. These nutrients are vital for the plant’s growth and reproduction.
Insects and small fish play a critical role in the nutrition of pitcher plants. They provide a rich source of nutrients that the plant can’t obtain from the soil. The plant lures its prey with a sweet-smelling nectar. Once the prey falls into the plant’s trap, it is unable to escape due to the slippery walls and drowns in the liquid at the bottom of the pitcher.
The plant then uses enzymes and bacteria to break down the prey, releasing nutrients that are absorbed into the plant. This process allows the plant to obtain nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, which are essential for its growth and development.
In conclusion, the carnivorous diet of pitcher plants provides them with essential nutrients that they can’t obtain from the soil. This unique adaptation allows them to survive in nutrient-poor environments where other plants can’t thrive. The role of insects and fish in their nutrition is crucial, providing a rich source of nutrients that are vital for the plant’s growth and reproduction.
Case Studies: Pitcher Plants in Action
Let’s delve into the fascinating world of pitcher plants and see them in action. We will explore two unique case studies that highlight the diversity of their diets.
Examples of Pitcher Plants’ Diets
-
Case study 1: The bug-eating pitcher plant
The bug-eating pitcher plant, also known as Nepenthes alata, is a fascinating example of nature’s ingenuity. This plant has evolved to trap and consume insects to supplement its nutritional needs. Its pitcher-shaped leaves are filled with a sweet-smelling nectar that attracts unsuspecting insects. Once an insect lands on the slippery rim of the pitcher, it slides into the trap, where it is digested by the plant’s enzymes.
According to a study, this plant can consume up to 6,000 insects in a year! This case study clearly demonstrates how pitcher plants have adapted to their nutrient-poor environments by becoming carnivorous.
-
Case study 2: The fish-eating pitcher plant
Yes, you read that right! Some pitcher plants have been found to eat small fish. The Nepenthes hemsleyana, a species found in Borneo, is known to trap and consume small fish and tadpoles. The plant’s large, deep pitchers are filled with water and act as a deadly trap for aquatic creatures. The fish are lured into the pitcher by the plant’s sweet nectar and are unable to escape due to the slippery walls of the pitcher.
This case study is a testament to the incredible adaptability of pitcher plants. It’s a clear example of how these plants have evolved to make the most of their environment.
These case studies provide a glimpse into the fascinating world of pitcher plants. From bugs to fish, these carnivorous plants have evolved unique strategies to survive in nutrient-poor environments. Stay tuned for more insights into the world of carnivorous plants!
Key Takeaways: Understanding Pitcher Plants’ Diets
As we delve into the fascinating world of pitcher plants, let’s summarize the key points about their diets. This will help us understand how these unique carnivorous plants survive and thrive in their natural habitats.
- Importance of Diet Variation for Pitcher Plants
- Impact of Diet on Pitcher Plant Growth and Survival
Pitcher plants are not just carnivorous; they are also opportunistic. They have a varied diet, which is crucial for their survival. Unlike most plants that rely on photosynthesis, pitcher plants supplement their nutrition by consuming insects, spiders, and sometimes even small animals. This diet variation allows them to survive in nutrient-poor soils where other plants struggle to grow.
The diet of a pitcher plant directly impacts its growth and survival. A study showed that pitcher plants that consumed a diet rich in insects grew significantly larger and healthier than those that didn’t. This is because insects provide essential nutrients, like nitrogen, that are scarce in the soils where these plants typically grow. Therefore, a nutrient-rich diet is key to the survival and growth of pitcher plants.
In conclusion, the diet of pitcher plants is a fascinating topic that reveals much about their unique survival strategies. By understanding their diets, we can better appreciate these remarkable plants and their role in the ecosystem.
Conclusion: The Fascinating World of Carnivorous Plants
As we wrap up our exploration into the captivating world of carnivorous plants, we focus our attention on the pitcher plant, a standout in this intriguing group. These plants have evolved to thrive in environments where most would struggle, turning to a diet that sets them apart from the majority of their green counterparts.
- Recap of pitcher plants’ unique dietary habits
- Final thoughts on the role of diet in the life of a pitcher plant
The pitcher plant, named for its distinct pitcher-shaped leaves, has developed a unique way of feeding that allows it to survive in nutrient-poor soil. Instead of relying solely on the process of photosynthesis like most plants, pitcher plants have turned to a carnivorous lifestyle. They attract, trap, and digest insects and other small creatures, extracting essential nutrients directly from their prey. This remarkable adaptation has allowed them to flourish where other plants cannot.
The diet of a pitcher plant plays a pivotal role in its life. It’s not just about survival, but also about thriving in their unique environments. The nutrients they extract from their prey support their growth and reproduction, making them a successful species in their habitats. Their dietary habits also impact the ecosystem around them, controlling the insect population and contributing to the biodiversity of their habitats.
In conclusion, the world of carnivorous plants, particularly the pitcher plant, is a testament to the adaptability and resilience of nature. These plants have turned the tables on the traditional plant diet, proving that in the struggle for survival, innovation is key. The next time you come across a pitcher plant, take a moment to appreciate its unique dietary habits and the role they play in its life and the ecosystem as a whole.








