Introduction to Pitcher Plants
Welcome to the fascinating world of pitcher plants! These unique plants, unlike most others, have evolved to thrive in nutrient-poor soils by catching and consuming insects. Let’s dive in and learn more about these incredible plants.
- Overview of Pitcher Plants
- Understanding the Unique Traits of Pitcher Plants
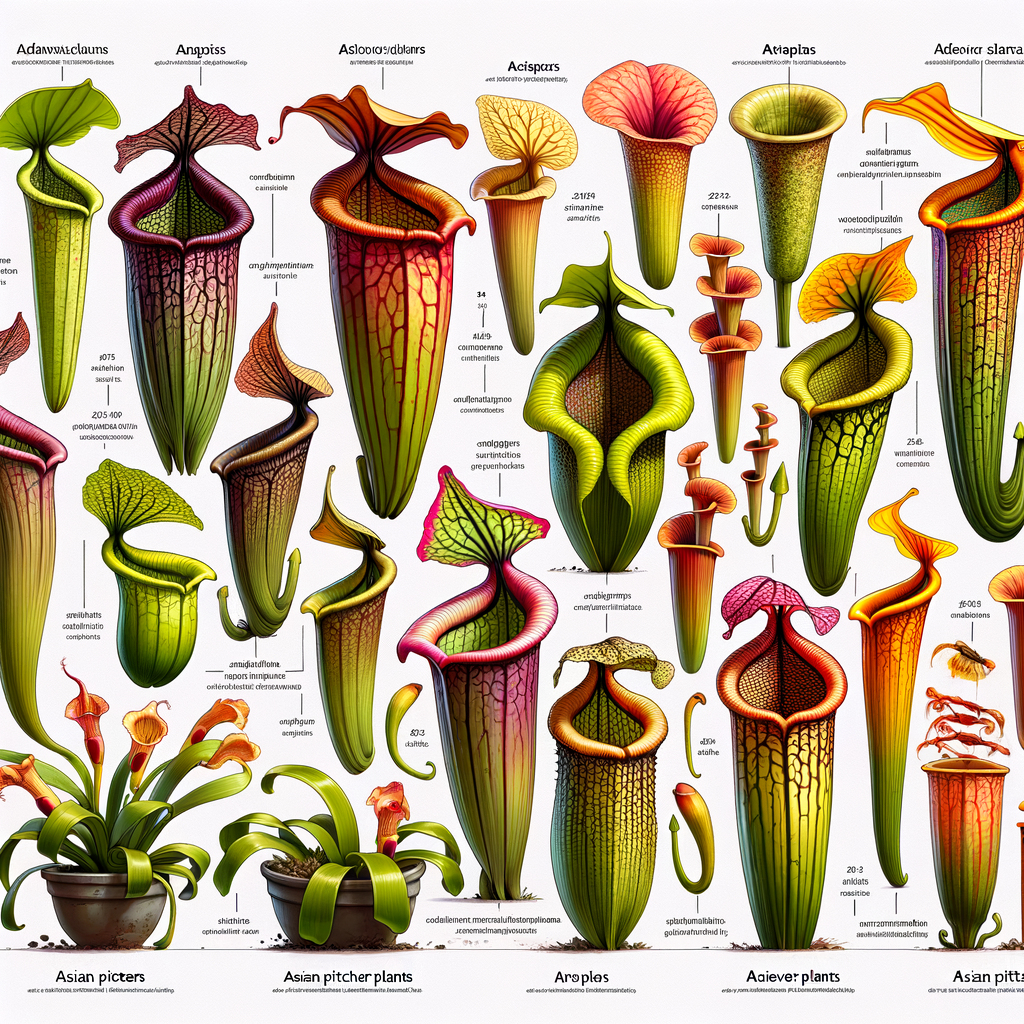
Pitcher plants belong to several different carnivorous plant species that have one thing in common – a unique, modified leaf structure that resembles a pitcher. This ‘pitcher’ is not just for show; it’s a cleverly designed trap for unsuspecting insects.
These plants are found in various parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia. Despite the harsh environments they inhabit, pitcher plants are remarkably adaptable and have evolved to survive and thrive.
What sets pitcher plants apart from other plants are their unique traits. The most notable of these is their carnivorous nature. Unlike most plants that get their nutrients from the soil, pitcher plants get their nutrients from insects they catch in their pitcher-like leaves.
These leaves are filled with a sweet-smelling nectar that attracts insects. Once an insect lands on the slippery rim of the pitcher, it’s only a matter of time before it slips and falls into the liquid-filled trap below. The plant then uses enzymes to break down the insect and absorb its nutrients.
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s delve deeper into the world of pitcher plants, starting with a spotlight on Asian pitcher plants. Stay tuned!
Species Spotlight: Asian Pitcher Plants
-
Introduction to Asian Pitcher Plants
Asian Pitcher Plants, scientifically known as Nepenthes, are a fascinating species of carnivorous plants native to the tropical regions of Asia. These plants have a unique way of trapping their prey. They produce a sweet nectar that attracts insects. Once the insects land on the slippery rim of the plant’s pitcher-shaped trap, they slide into the digestive liquid at the bottom where they are consumed. This is how the Asian Pitcher Plant gets its nutrients, making it an exciting example of nature’s ingenuity.
-
Characteristics of Asian Pitcher Plants
Asian Pitcher Plants are known for their distinct pitcher-shaped traps, which can vary in size from tiny to large enough to trap a small mammal. They have a lid over the opening of the pitcher to prevent rainwater from diluting the digestive fluid inside. The color of these plants can range from green to red, often with beautiful patterns and spots. The plant’s leaves, which evolve into the pitcher traps, are typically long and slender.
Characteristic Description Shape Pitcher-shaped traps Size Varies from tiny to large Color Green to red, often with patterns and spots Leaves Long and slender Asian Pitcher Plants are not just unique but also play a vital role in their ecosystem. They help control insect populations and provide habitats for several small creatures, making them an essential part of the biodiversity in their native regions.
Understanding Asian Pitcher Plants
Asian Pitcher Plants are fascinating species of carnivorous plants that have intrigued scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. Let’s delve deeper to understand their unique traits and common varieties.
- Unique Traits of Asian Pitcher Plants
- Trap Mechanism: These plants have a specialized trap mechanism. The pitcher-like structure filled with digestive fluid is actually a modified leaf. This ‘pitcher’ traps and digests insects, providing the plant with essential nutrients.
- Size and Color: Asian Pitcher Plants can vary greatly in size and color. Some species have pitchers that are only a few centimeters in size, while others can grow up to 35 centimeters. They can be green, red, purple, or even black, often with striking patterns.
- High Altitude Adaptation: Many species of Asian Pitcher Plants are adapted to grow in high altitude areas. They can thrive in areas over 1000 meters above sea level, a trait not commonly found in other carnivorous plants.
- Common Varieties of Asian Pitcher Plants
Asian Pitcher Plants, scientifically known as Nepenthes, are known for their unique and intriguing traits. Here are some of their most distinctive features:
There are over 130 species of Asian Pitcher Plants, each with its own unique characteristics. Here are a few common varieties:
| Species | Description |
|---|---|
| Nepenthes alata | This species is known for its slender, elongated pitchers and wide distribution across Southeast Asia. |
| Nepenthes rajah | Recognized for its large size, this species can trap not only insects but also small vertebrates. It’s native to Borneo. |
| Nepenthes mirabilis | Often called the ‘common pitcher plant’, this species is widespread and highly variable in appearance. |
In conclusion, Asian Pitcher Plants are a captivating group of carnivorous plants with a variety of unique traits and species. Their ability to adapt and thrive in diverse environments is a testament to the wonders of nature.
Pitcher Plants Differences: Asian vs Other Species
Let’s dive into the fascinating world of pitcher plants, specifically focusing on the differences between Asian pitcher plants and other species from around the globe.
- Comparing Asian Pitcher Plants with Other Species
- Key Differences in Characteristics
Asian pitcher plants, known scientifically as Nepenthes, are unique in their own right. They are predominantly found in Southeast Asia, including Borneo, Sumatra, and the Philippines. Unlike their counterparts, Asian pitcher plants are mostly climbers, using their tendrils to reach for the sunlight in the forest canopy. They also have a wide variety of pitcher shapes and colors, from deep reds to vibrant greens.
On the other hand, other species of pitcher plants, such as the North American Sarracenia or the South American Heliamphora, display different characteristics. For instance, Sarracenia species are mostly ground-dwelling plants that prefer open, sunny habitats. They have tall, slender pitchers with a hood-like structure at the top. Heliamphora, native to the tepuis of South America, have a simpler, more tubular shape, and often grow in clusters.
One of the key differences between Asian pitcher plants and other species lies in their trapping mechanisms. Asian pitcher plants use a slippery, waxy coating on the inner surface of their pitchers to trap insects. This is complemented by a sweet, nectar-like substance that lures the prey.
Contrastingly, North American pitcher plants use a combination of scent, nectar, and visual cues to attract prey. They also have downward-pointing hairs inside their pitchers, which prevent the prey from escaping. South American pitcher plants, or Heliamphora, use a similar strategy, but their pitchers are filled with rainwater, which drowns the prey.
Understanding these differences helps us appreciate the diversity and adaptability of pitcher plants. Each species has evolved unique strategies to survive in their specific habitats, showcasing the wonders of nature.
Case Study: Asian Pitcher Plants vs Other Species
Let’s take a closer look at how Asian Pitcher Plants compare with other species from different parts of the world. We will focus on North American and South American Pitcher Plants.
-
Example 1: Asian Pitcher Plants vs North American Pitcher Plants
Asian Pitcher Plants, also known as Nepenthes, are unique in their own way. They are known for their large and colorful pitchers, which can hold up to two liters of water. On the other hand, North American Pitcher Plants, or Sarracenia, are smaller in size and their pitchers are usually green or red.
Characteristics Asian Pitcher Plants North American Pitcher Plants Size of Pitchers Large Small Color of Pitchers Varied Green or Red Water Capacity Up to 2 liters Less than 1 liter -
Example 2: Asian Pitcher Plants vs South American Pitcher Plants
South American Pitcher Plants, also known as Heliamphora, are known for their elegant, elongated pitchers and bright colors. However, they are smaller than Asian Pitcher Plants and can’t hold as much water. Asian Pitcher Plants, with their large size and water-holding capacity, are more adaptable to different environments.
Characteristics Asian Pitcher Plants South American Pitcher Plants Shape of Pitchers Varied Elongated Color of Pitchers Varied Bright Colors Adaptability High Low
In conclusion, while all pitcher plants share some common characteristics, there are also significant differences between them. Asian Pitcher Plants, with their large size and adaptability, stand out among other species.
Conclusion: The Uniqueness of Asian Pitcher Plants
As we wrap up our exploration of the fascinating world of pitcher plants, it’s clear that Asian Pitcher Plants stand out in their own unique way. Let’s take a moment to recap their distinctive characteristics and key takeaways when compared to other species.
- Recap of Asian Pitcher Plants Characteristics
- Key Takeaways on Asian Pitcher Plants vs Other Species
Asian Pitcher Plants, also known as Nepenthes, are renowned for their large and colorful pitchers. These plants are carnivorous, using their specialized pitchers to trap and digest insects. Unlike other pitcher plants, they have a lid that prevents rainwater from diluting the digestive juices inside the pitcher. They also have a unique adaptation – a waxy coating inside the pitcher that makes it slippery for insects, ensuring their prey can’t escape.
When compared to other species, Asian Pitcher Plants are more diverse in terms of size, color, and shape of their pitchers. They are also found in a wider range of habitats, from the tropical rainforests to the highlands of Southeast Asia. Unlike some other pitcher plants, Asian Pitcher Plants can survive in less acidic soil, making them more adaptable to different environments.
In conclusion, Asian Pitcher Plants are a unique and fascinating species. Their distinctive characteristics and adaptability make them stand out among other pitcher plants. They are a testament to the incredible diversity and adaptability of nature. As we continue to explore and understand these amazing plants, we can only marvel at the wonders of the natural world.








